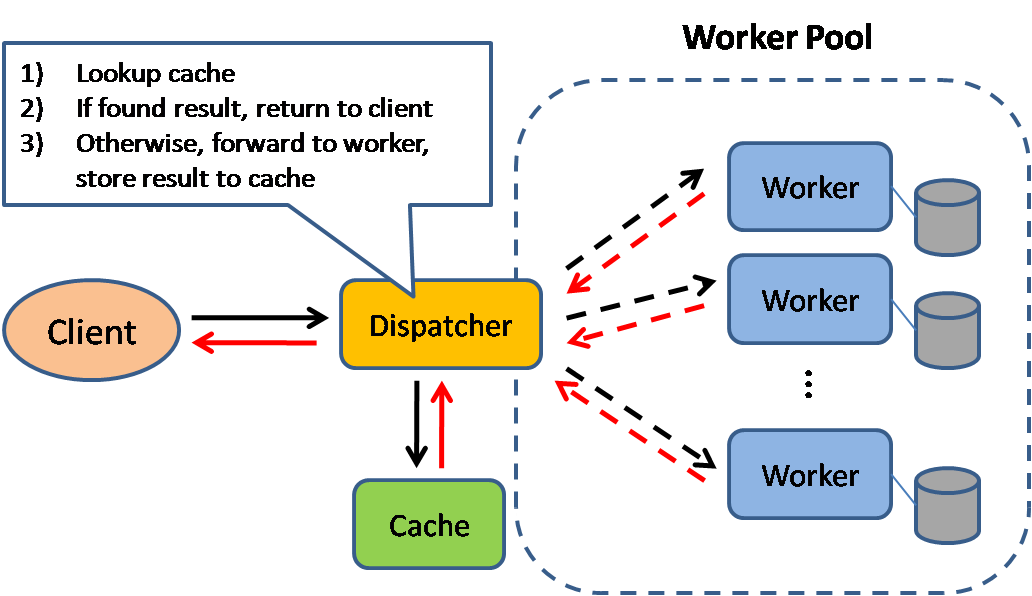
Using a cache tends to improve read times and can also reduce the load on backend servers and databases.
In the above example, a dispatcher service reads a client request then checks whether the data requested is already in a cache. If so, the data is returned. Otherwise, the client request is forwarded to a worker which queries the database. The data is returned from the worker to the dispatcher, which then stores the data in a cache under some pre-defined criteria.
Databases generally perform better when read and write operations are evenly spread across partitions or shards. Certain popular items can cause bottlenecks. As such, putting a cache in front a database can help absorb uneven loads and prevent traffic spikes.